
Laser radiation
For most of the continuous laser sources, laser radiation is made of multiple narrow frequency lines, at specific wavelengths corresponding to energetic transitions of the amplifying medium.
In the case of pulsed sources, light radiation is constituted of many frequencies contained in a spectral envelope, whose width can be of up to hundreds of nanometers.
For example, a source delivering light pulses of 10 fs emits a radiation whose spectral width is equal to 90 nm.
The light emitted by a laser is in the “optical” domain of the electromagnetic spectrum. It includes wavelengths from 180 nm to 1 mm. Optical radiation is conventionally classified as follows :
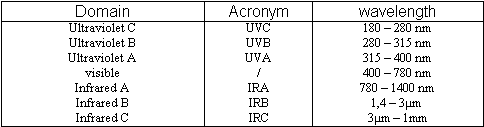
Laser technology is still experiencing great innovations concerning simultaneously the beam characteristics, the high powers, but also the size of the source system. This explains the spread of laser technology to diverse domains, such as telecommunications, medicine, fundamental physics... Consequently to this diversity of applications, one understands the necessity to train laser sources users to laser safety.