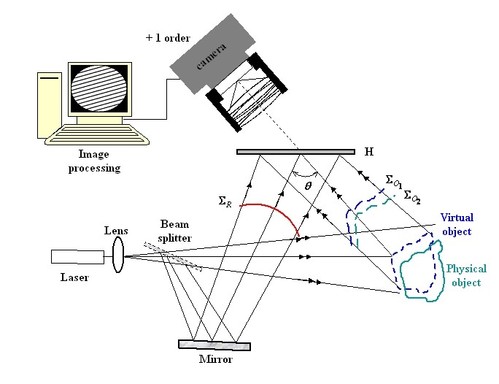
The Experimental Set-up
The experimental device is conventional since it is being used to record a hologram of an object at rest (figure 6). The light source must equally be spatially and temporally coherent except if a perfect balance between the object and the reference optical paths can be assured.
An impulse laser can also be used for the recording, which allows for very short exposure times.
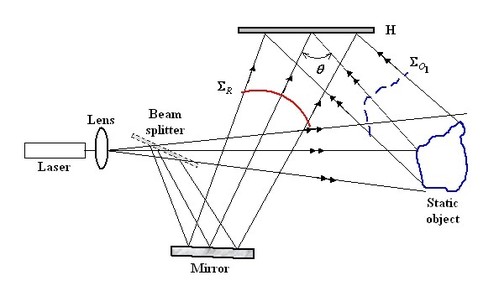
Figure 7 shows the principle of the real time method. At the same time, the hologram is illuminated with the reference beam and the object is illuminated with the object beam. The reference beam diffracts onto the hologram and reconstructs the previously recorded object. At the same time, the object beam illuminated he real object and this then interferes with the virtual wave reconstructed by diffraction. The observer can directly visualise he reconstructed object and the interference fringes which modulate its amplitude. However, with a view to a quantitative exploitation, visual observation is replaced with an observation using a camera or a video camera. It is sufficient to place the sighting of the lens towards the +1-order and to focus on the object as shown in figure 7.