
Tunablecavity Fabry-Pérot laser
The possibility of nanopositioning is essential for applications such as the tunable laser cavities for which the specific dimensions are in the order of the laser wavelength. This necessity allowed a good combination between MOEMS nanopositioning capacities and VCSEL technology. VCSEL were invented during the late 1980s, they were a means to obtain solid-state lasers to give out light vertically compared with a substrate, which is better for a high number of applications in lighting, optical networking, etc.
In initial structures, the VCSEL upper mirror was a DBR (Distributed Bragg Reflector). In the Microsystems setup described in the picture below (from 1995), the reflector is linked to a mobile clamped beam structure, able to grant the resonating wavelength until 15nm with a weak voltage control of approximately 5 to 7V.
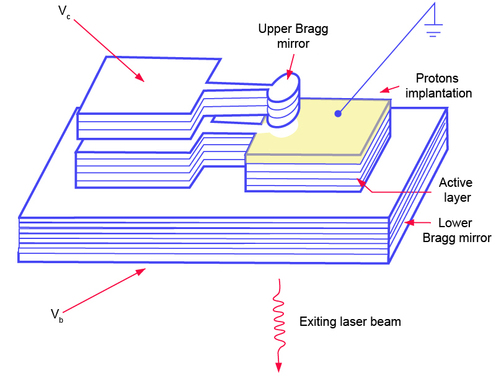
Since the first experiences, acordability has been improved in order to cover the 1530-1620 nm range of DWDM communications wavelengths.