
Introduction
They are made of transparent medium of index n between two diopters of radius R1 et R2. The lens axis goes through the curvature centres of the sides. This axis cuts the diopters at their vertex S1 and S2. e = S1S2 is the thicken at the vertex of the lens.

Diopters refracting power vare respectively :
Cv1 = (n-1)/R1 et Cv2 = (1-n)/R2
The lens is in the air, following (29) the lens refracting power Cv is :
Cv = 1/f ' = -1/f.
For certain types of lenses (ophthalmic lenses), Cv is expressed in dioptrie rated δ (1.δ = 1.m-1).
Gullstrand's formula gives the refracting power Cv of a lens as the associaiton of two diopters.
We get :
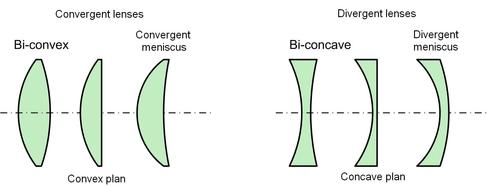
Convergent lenses are thicker at their centre than on their sides, inversely divergent lenses are thicker on their sides.