Fundamentals of geometrical optics

Spherical mirrors
A spherical mirror is a concave or convex reflecting surface defined by the centre of curvature C and a vertex S located on the surface. The curvature ray is
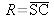 .
.

Figure 25
[zoom...]
Let us consider a point A of the line SC. A luminous ray arising from A reflects itself on a point I of the mirror et cuts its line SC in A'. If we carry out the same operation as for the diopters, we have :
And
Or sin(i) = - sin(i ') therefore :
The expression below is analogeous to the diopters' by replacing n' by –n. We therefore have, as for the diopters,
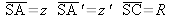 :
:
inchangé
toujours négatif
These formula are identical whether the mirror is concave or convex.
The conjugation formula is symetrical in
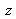 and
and
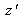 . If A' is image of A, A is image of A'.
. If A' is image of A, A is image of A'.